Most women have a 28-day cycle and ovulate on day 14. However, the odds change across age groups hence you have most likely:
- 29-day cycle, ovulation on day 15 between 18 and 24 years
- 28-day cycle, ovulation on day 14 between 25 and 39 years
- 27-day cycle, ovulation on day 12 above 40 years
These are the findings of a 2020 study that analyzed 18761 cycles using a mobile app and LH urine tests.
More importantly, the most fertile day is 2 days before ovulation. For centuries, we thought that ovulation occurred on the most fertile day. However, you are approx. five times more likely to get pregnant two days before ovulation than on the day of ovulation. And that’s a big difference!
Ovulation
At ovulation, the egg matures, the follicle ruptures, and the ovary releases the egg. Then it travels to the uterus through the fallopian tube. If sperm cells are waiting here, one of them can fertilize the egg. The egg dissolves in 12-24 hours after ovulation if it is not fertilized. But if the egg is fertilized, an embryo begins to develop, which can implant in the uterus a week later, and the pregnancy can begin.
Actual day of ovulation
If we want to know more about the ovulation day we can rely on another 2020 study. The researchers wanted to determine the exact day of ovulation. Therefore, they asked 32 595 women to contribute to the study with their data. They analyzed urine tests tracking luteinizing hormone (LH) in 75 981 cycles. In fact, when the level of LH in the urine rises, ovulation occurs the following day. From this they concluded on the actual ovulation day.
The researchers examined the cycle-lengths one by one. Most women had a 28-day cycle and ovulation on day 15. The probability of actual ovulation compared to the length of the cycle:


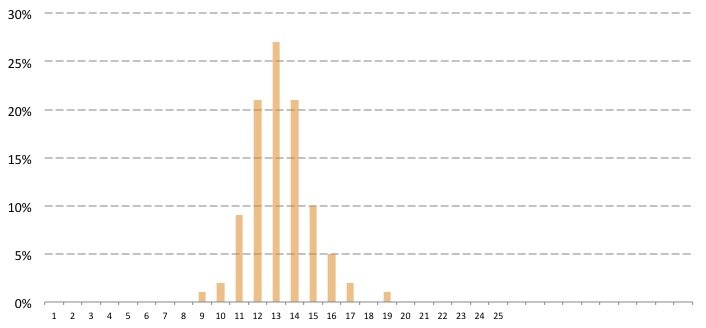


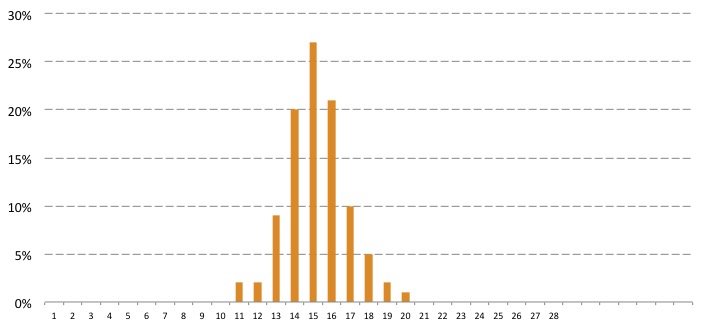







The researchers came to the conclusion that the actual day of ovulation depends greatly on the length of the cycle and varies considerably within it. The actual days were compared with the predictions of the calendar method. They came to the conclusion that it cannot give an accurate forecast based on the calendar. Therefore, it is worth relying on other methods if one wants to determine the fertile period.
Signs of ovulation
In humans, the fertile period is hidden. That is, there are no clear signs and it is difficult to say exactly when ovulation is. Nevertheless, sexual desire, smell, skin, breast sensitivity, breathing, heartbeat, smell, movement and external changes can also indicate its approach. Moreover, at this time, the taste may also change in favor of a more masculine appearance (wider jawline, shoulders, thicker fur). In addition, during follicular rupture, there may be a stinging sensation around the ovary, i.e. middle age pain, which may be accompanied by dizziness, headache and spotting bleeding.

It is worth noting these signs in an application. If one learns and pays attention to them, one can recognize the fertile period and ovulation over time. You have to take your time because not everyone or every cycle has the same signs. People who use hormonal contraceptives do not have cycles and do not have symptoms.
Let’s go through the most important signs and look at the most commonly used tests.
Cervix, cervical mucus and saliva

Cervix
The upcoming ovulation is indicated by the position and softness of the cervix. The cervix produces cervical mucus, which is the most reliable sign of fertile days. Conception requires not only sperm and egg, but also semen and cervical mucus. so that the sperm cells can swim up and stay alive. From the cervix, they continue to swim through the uterus and wait in the fallopian tube. When ovulation occurs, conception takes place here.
Cervical mucus
The amount, color and texture of the cervical mucus changes depending on the hormones. Most sperm cells die immediately in the acidic vagina. However, before ovulation (in the follicular phase), different types of mucus are produced under the influence of estrogen, and they also have a different biochemical composition. In the stretchy, slightly alkaline and nourishing cervical mucus, the sperm cells can easily swim up through the cervix to the fallopian tube. Abnormal sperm cells, on the other hand, get stuck in the cervical mucus. Only the fittest survive for 3 days (rarely up to 5 days). Since a more viable sperm fertilizes the egg, there is a greater chance of pregnancy.
If you air-dry the fertile cervix, you can see crystals according to a research under a microscope.

After ovulation (in the luteal phase), the corpus luteum is formed from the follicle, which no longer produces estrogen, but progesterone. The cervix produces less and less cervical mucus, and it is no longer transparent, but sticky, because its water content is low. Its biochemical composition helps the adhesion of antibodies and antimicrobial peptides. The mucins that make up the mucus form a dense mesh, plugging the cervix and preventing bacteria and microbes from entering the uterus. Sperm cells only survive in this for a few hours. In this case, crystals are no longer visible.
During the cycle, the composition and concentration of electrolytes in the cervical mucus, as well as in the saliva, changes under the influence of estrogen and progesterone. Devices that measure changes in electrolyte levels in the vagina and mouth are now available. Based on these, you can determine the fertile period.

Saliva
In most women, salivary crystals can be seen in dry saliva samples during the fertile period. Their shape changes as the cycle progresses in the same way as in dry cervical mucus. Fern-shaped crystals appear a few days before ovulation and disappear when the egg matures. However, this doesn’t work for everyone because anything that affects estrogen levels in the body can affect the results. These may include age, medications, infections, breastfeeding, and pregnancy.

For those who can use the saliva ovulation test, they can easily track their most fertile days. Those who are more skilled can take a sample from the cervical mucus for the test, but sampling through the vagina is difficult. Therefore, for home use, this method was only officially recognized for the saliva test.
The Babyndex app is the first to automatically recognize the fern patterns of saliva crystals. These appear before ovulation on fertile days, while the chance of getting pregnant is up to five times higher than on the day of ovulation. The app stores the results and thus helps to use the natural fertility awareness method. You only need a microscope to view the crystals.

Basal body temperature
Before ovulation, the basal body temperature is lower, but after ovulation it rises by a few tenths of a degree. From this, you can deduce the day of ovulation, but it is only worth using this method for those who have a regular cycle. Since you only need a thermometer and to measure the body temperature before getting up in the morning, many mobile applications have some basic function for this.

Most mobile applications do not predict ovulation based on the calendar method, but on the basis of urine or body temperature tests. With a regular cycle, they can also predict the fertile days before the expected ovulation. Of course, with an irregular cycle, predictions based on ovulation do not work.
We have to mention that one fertility app manufacturer released their observations in 2019. They had the body temperature data of many cycles available, but they did not examine randomly selected women, because they recommend the application to those who have regular cycles. Therefore, the results do not show the average cycle, but they are very interesting. Similarly to the research above, 35-year-olds ovulate on day 16, and 25-year-olds – who have longer cycles – ovulate on day 18.
Urine
Urine tests can detect a sudden increase in luteinizing hormone (LH). The pituitary gland produces the LH and it plays a key role in ovulation. The rise in the level of LH in the blood initiates the release of the egg, which occurs 24-36 hours later. The LH surge in the urine can be detected approx. half a day later. Therefore, based on the test, you can expect ovulation for the next day, when fertility is already lower.

Test strips that can be dipped into the urine sample are available with different sensitivities. The result can be read in a short time. However, these tests do not always show accurate results. An elevated LH level does not necessarily mean that ovulation will occur.
Ultrasound
Ultrasound can help determine the exact time of ovulation. Transvaginal ultrasound allows doctors to see the ovaries, measure the size and number of follicles, identify when the dominant follicle is selected, and see when the egg is released from the ovary into the fallopian tube. This procedure is the most accurate way to determine the most fertile days, but it is only performed by professionals and is expensive.

The process of ovulation

1-2 weeks before ovulation
- Cervical mucus appears, the cervix produces it in small quantities at the beginning, and it is not transparent, thick and sticky.
- Depending on the rise in estrogen levels, more and more cervical mucus is produced and its composition changes, becoming increasingly transparent, moist, stretchy, and slippery.
2 days before ovulation
- Cervical mucus is abundant, it resembles egg whites, in which sperm cells can easily swim.
- The cervix becomes longer, more advanced, more open and softer.
- Under a microscope, fern-shaped crystals can be seen in dry cervical mucus and saliva samples.
- The estradiol metabolite can be detected with more expensive urine tests, but its accuracy is low.
On this day, you have the highest chance of getting pregnant. However, the majority of the most commonly used urine and thermometer tests do not indicate this. Tests that work based on changes in cervical mucus and saliva give an indication in real time. Estradiol metabolites can also be detected in urine in real time. These tests are not widespread because there are many things that affect the level of estrogen. However, if someone has a regular cycle, you can use a mobile application to know when these few days will come based on the recorded data of urine and thermometer tests. With an irregular cycle, mobile applications do not work.
1 day before ovulation
Most of the time, luteinizing hormone is released into the bloodstream at dawn (LH surge), and ovulation occurs within the next 24-36 hours. Blood tests can detect LH almost immediately, but urine tests can be detect LH approx. half a day later. Estrogen levels are constantly decreasing, while progesterone levels are increasing.
- The core body temperature drops a little.
- The composition of the electrolytes changes in the cervical mucus and saliva, which is why different types of crystals are visible in the dry samples.
- LH can be detected with urine tests and its accuracy is high.
Most commonly used urine tests indicate this day. However, those who want a baby have only one fertile day left.
On the day of ovulation
Progesterone production continues to increase and LH and FSH levels decrease as the egg is expelled from the ovary. If there are sperm cells in the fallopian tube, the egg can be fertilized up to 12 (rarely 24) hours after ejection. If it implants after that, it can lead to pregnancy.
- Mid-term pain on the right or left side, when the egg is ejected from the ovary (sometimes even several), in addition to bloating, possibly light bleeding, sensitivity of the breasts, sensitivity to smells, dizziness, headache.
- Electrolyte levels change and crystals change shape and become less visible.
After ovulation
After ovulation, the remaining follicle turns into a corpus luteum and produces an increasing amount of the hormone progesterone. As a result, the uterine wall thickens and waits for the potentially fertilized egg to implant. We can say that the uterus is an eternal optimist, because it prepares for pregnancy in the same way every month. If the egg is fertilized, it can implant in the lining of the uterus and pregnancy can begin. If fertilization fails, the ovum is reabsorbed, the corpus luteum withers, and the lining of the uterus detaches and leaves the body with monthly bleeding. If embedded, then pregnancy starts.
- The morning basal body temperature rises one or two days after ovulation, and this can also be observed with a simple thermometer.
Reasons for failure to ovulate
If ovulation is missed during the cycle, it may be due to some hormonal disease. In these cases, ovulation can be induced with appropriate treatment. Ovulation is also missed if the ovaries are exhausted at menopause, i.e. at the end of the fertile age. A 2013 study only looked at anovulatory cycles in healthy, regularly menstruating women. They came to the conclusion that many healthy women do not ovulate (7.6%).
The most common decease is PCOS, but there are other causes of ovulation failure, such as:
- sedentary lifestyle, insomnia, stress,
- sudden weight loss or weight gain, incomplete diet, malnutrition,
- diseases, bad environmental factors,
- age, genetics.
PCOS
The most common hormonal disorder is polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS). Patients with PCOS have difficulty getting pregnant because follicles form in the ovaries, but the egg is not expelled. A few decades ago, this disease was hardly encountered, but now it has become one of the leading causes of infertility. It affects more than 10 percent of women in developed countries. Since it is a serious hormonal, metabolic and reproductive disorder, early detection is important. Complications may include:
- infertility,
- obesity, cardiovascular diseases,
- type 2 diabetes,
- (non-alcoholic) fatty liver disease,
- endometrial cancer,
- maternal/fetal health complications,
- psychosocial disorders.
Ovulation can also be checked at home with LH and progesterone tests and thermometers. If you miss ovulation, it’s worth seeing a doctor, who can determine the real cause and suggest treatment options.
Multiple ovulations at once
Very rarely, ovulation can also occur during pregnancy, and it is even possible to become pregnant. This phenomenon is called superfetation, and extremely few cases are known. A simultaneous pregnancy is when the pregnant woman is implanted both inside the uterus and outside the uterus at the same time, and thus an intrauterine and an extrauterine pregnancy start to develop at the same time.
Ovarian reserve
In each cycle, several eggs begin to mature at the same time, but a dominant one is selected. This healthy egg matures, while the rest wither away. In 1-2 percent of cycles, two or even more follicles ripen at the same time, and several eggs are expelled from the ovary. In this case, there is a chance of a multiple egg pregnancy. From the start of menstruation to menopause, a total of approx. 400 eggs mature.
Baby girls are born with several million eggs. This number is rapidly decreasing:
- at the start of menstruation approx. 300 thousand,
- at the age of twenty, approx. 200 thousand,
- at the age of thirty approx. 100 thousand, and
- at the age of forty, only a few thousand eggs are available, but even one is enough for pregnancy.
The Müllerian inhibitory hormone (AMH) test shows how many eggs are in a woman’s ovaries.
Before getting pregnant
If you want a baby, you should start taking a pregnancy vitamin (also known as a fetal protection multivitamin) at least 1-2 months before trying. The 4-8 weeks after conception are very important for the baby’s health. But at that time, many expectant mothers do not even know that they are pregnant, and the body’s vitamin reserves cannot be replenished at lightning speed. This is precisely why it is necessary to fill up the body’s vitamin stores before the long-awaited fertilization takes place.
Ovulation after birth
We still need to talk about ovulation after childbirth. When the regular cycle starts again after giving birth varies from person to person. Women who breastfeed for a long time usually ovulate again later, but there are quite a few exceptions. The follicular maturation can occur even during breastfeeding without menstruation. It is recommended to discuss the protection options with the gynecologist at the six-week check-up, if we do not want to get pregnant again too soon.
